For database administrators and developers, understanding and analyzing SQL queries to improve database performance and optimize data integration processes is extremely important.
In this post, I will proceed by giving examples from PostgreSQL. However, since it is the basic subject of the relational database structure, the same queries and situations are valid in technologies such as MySQL, SQL Server (MS SQL), etc., even if some concepts differ.
What is Query Analysis?
Query analysis in SQL is a process to evaluate and improve the performance of running queries. This process involves analyzing the query runtimes, disk and memory usage, index usage, and more in detail. Query analysis helps you identify and resolve database performance issues.
EXPLAIN ve EXPLAIN ANALYZE
One of the most basic tools for analyzing queries in SQL is the EXPLAIN command. This command displays the plan for a particular query but does not actually run the query. EXPLAIN ANALYSE does the same thing as EXPLAIN, but also reports the actual execution time of the query. Let's examine a query with EXPLAIN ANALYSE.
EXPLAIN ANALYSE SELECT * FROM todos
WHERE tenant_user_id = 1
AND planned_at >= '2024-03-03T21:00:00.000Z'
AND planned_at <= '2024-03-04T20:59:59.999Z'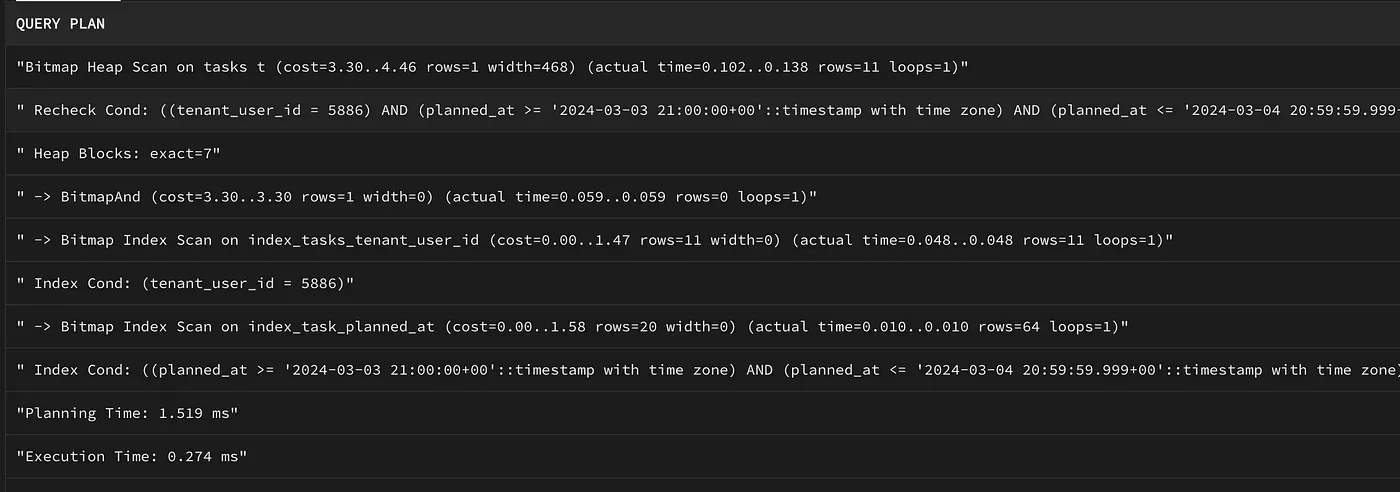
You can examine the query output with the following information.
Cost Information: cost values show the estimated costs calculated as part of database optimization. Lower costs generally mean better performance.
Actual Time Information: actual time values show the actual time spent on each step. This helps you understand how long each step took and which parts of the query took the most time.
Rows (Satır) Bilgileri: rows values show the estimated or actual number of rows in each step. This helps you understand the amount of data processed in each step and evaluate the performance of the query.
Index Usage: Expressions such as Bitmap Index Scan and Bitmap Heap Scan show index usage. It is important to pay attention to which indexes are being used and how the indexes are performing
Heap Blocks Information: The Heap Blocks value provides information about memory usage
Planning Time and Execution Time: Planning Time indicates the planning time of the query, and Execution Time indicates the execution time of the query. These values indicate how long it takes to plan and execute the query.
Data Type and Index Optimization
Using data types and indexes correctly in SQL can significantly affect performance. Especially when working with large data sets, it is important to choose the right data types and create the necessary indexes. To learn more about data types and indexes, you can read my article “Optimizing Database Performance: Index Selection”.
Conclusion
Performing query analysis in SQL is a critical part of optimizing database performance. Tools such as EXPLAIN and EXPLAIN ANALYZE can be used to examine query execution plans and identify performance issues. Proper use of data types and indexes can also improve performance. By performing query analysis in PostgreSQL, you can significantly improve your application performance.
Thank you for reading my post, I hope it was helpful to you 🙂
Good luck with your work…


